
The controller then adds these three values together to create the output.īelow we will dive into the proportional, integral and derivative as three separate equations, then add them together to create the output, but first, we need to talk about the user input values in the PID controller… the gain settings (P-Gain, I-Gain and D-Gain). The PID controller is continuously monitoring the error value, and using this value, calculates the proportional, the integral and the derivative values. The basic explanation of a PID controller. The error value is the value used by the PID controller to determine the how to manipulate the output to bring the process value to the set point.Įrror = Setpoint – Process Value PID Controller Explained! In cruise control, the output would be the throttle valve, in a heating system, the output might be a 3 way valve in a heating loop, or the amount of fuel applied to a boiler.
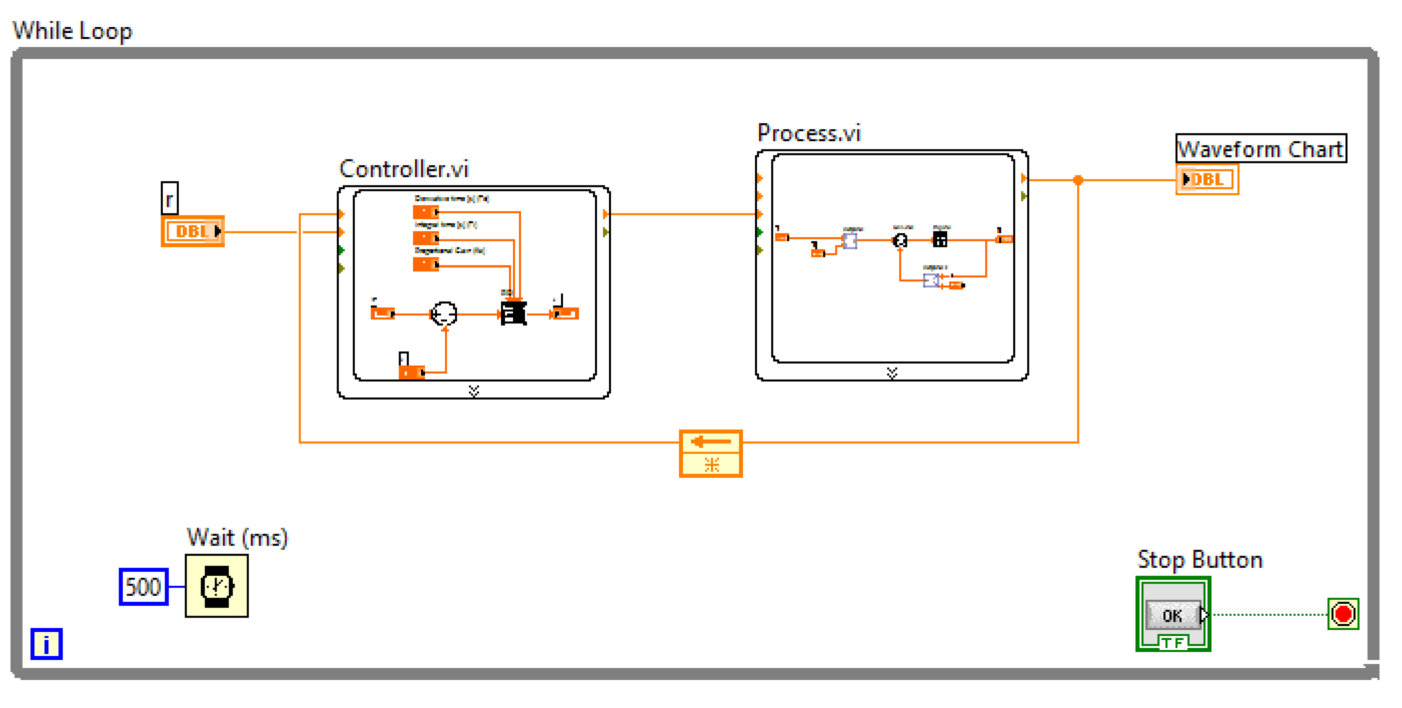
The output is the controlled value of a PID controller. For cruise control this would be the actual vehicle speed, or in a heating system, this would be the current temperature of the system. The process value is the value that is being controlled. The set point is normally a user entered value, in cruise control it would be the set speed, or for a heating system, it would be the set temperature.

And also the PID Simulator page to use a live PID Simulator!īefore we dive into the PID controller, there is a few terms that need defined: PID Controller Terms: Set Point See post “ WHAT IS A PID CONTROLLER?” for a basic example of a PID controller. A PID (Proportional Integral Derivative) controller works by controlling an output to bring a process value to a desired set point.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
